
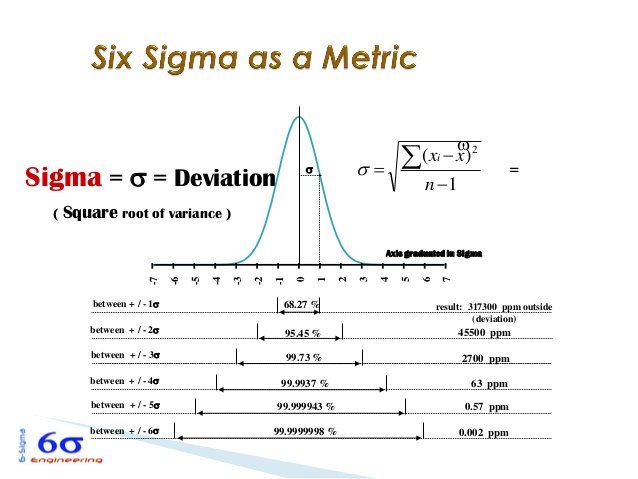
A six-sigma calculation has a 99.99966% accuracy, whereas a three-sigma calculation has a 99.73% accuracy. Since six sigma calculates six standard deviations from the mean, its value is usually more accurate than three sigma. Here are some differences between three sigma and six sigma: Accuracy Related: 7 Types of Statistical Analysis Techniques (And Process Steps) Three sigma vs. The director can implement new processes to shrink the standard deviation if they want to achieve six sigma accuracy. If 99.7% of the finished products fall within three standard deviations of the mean, then the product has accuracy on the three-sigma level. For example, if a company that makes tires has an accepted upper and lower limit for a certain tire, sampling the finished products and mapping their diameters on a normal curve can help the manufacturing director evaluate the error level. Related: 5 Ways To Find Outliers in Statistics (With Examples) To improve accuracyįor manufacturing and business processes, this calculation can help improve the quality of the finished product. If two days had much lower productivity than the average variation, the manufacturing director might investigate those days to find out what might have caused the slower pace. For example, a manufacturing company might map its production levels each day using this method. Using a calculation like three sigma can help you identify which data points fall outside of the normal distribution. While some outliers are easy to see on a plot of data points, others may not be as easy to detect. Outliers are data points that don't fit within the set parameters for a set of data.
2 SIGMA CALCULATION HOW TO
Related: How To Chart Upper Control Limit in Excel (With Formulas) To analyze outliers For instance, during a medical trial, if the majority of participants experience a positive improvement in their conditions to a certain degree, but two patients experience almost double improvement in their conditions, then it may be because of factors beyond the medication. This allows statisticians to identify any outliers in their data so they can adjust their data accordingly when their well-controlled environments don't account for certain results. Statisticians can use three sigma calculations to set the upper and lower control limits in statistical quality control charts, which create limits for business or manufacturing processes. Here are some reasons you might use this calculation: To set control limits Related: 50 Statistics Terms To Know (With Definitions) Uses for 3 sigma calculations

Three sigma follows the 68-95-99.7 rule, where 68% of the data falls within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% of the data within two standard deviations of the mean and 99.7% of the data within three standard deviations of the mean. Also referred to as the three sigma limits or empirical rule, this tool helps calculate the probability that a certain point falls within established parameters. Three sigma in statistics is a calculation that shows the bounds of data points that lie within three standard deviations from a mean in a normal distribution.

2 SIGMA CALCULATION PROFESSIONAL
In this article, we define three sigma in statistics, compare this calculation to six sigma, explain why you might use this calculation, share steps for calculating three sigma and provide an example of this calculation in a professional setting. Knowing how to calculate three sigma for a dataset can help you set control limits and produce more useful statistical reports. One of these calculations, called three sigma, can help determine if any outliers exist in a dataset when you're evaluating your collected variables. Statisticians use a variety of calculations when gathering and interpreting data from their studies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
